A4.8051 Communication Protocols:UART, RS232
In this tutorial, we are going to discuss the serial/UART communication of 8051. After understating the basics of 8051 UART module, We will see how to use the ExploreEmbedded libraries to communicate with any of the UART devices.
Contents
[hide]UART Registers
The below table shows the registers associated with 8051 UART.
| Register | Description |
|---|---|
| SCON | Serial Control Register |
| TCON | Timer Control Register for Baud Rate Generator |
| TMOD | Timer Mode Control for Baud Rate Generator |
| SBUFF | Serial Buffer holds the data to be transmitted and the data received |
UART Register Configuration
Now lets see how to configure the individual registers for UART communication.
| SCON | |||||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| SM0 | SM1 | SM2 | REN | TB8 | RB8 | TI | RI |
| SM0 | SM1 | Operation | Description | Baud Rate Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | Mode 0 | 8-bit UART | 1/12 the quartz frequency |
| 0 | 1 | Mode 1 | 8-bit UART | Determined by the timer 1 |
| 1 | 0 | Mode 2 | 9-bit UART | 1/32 the quartz frequency |
| 1 | 1 | Mode 0 | 9-bit UART | Determined by the timer 1 |
- SM2 - Serial port mode 2 bit, also known as multiprocessor communication enable bit. When set, it enables multiprocessor communication in mode 2 and 3, and eventually mode 1. It should be cleared in mode 0.
- REN - Reception Enable bit enables serial reception when set. When cleared, serial reception is disabled.
- TB8 - Transmitter bit 8. Since all registers are 8-bit wide, this bit solves the problem of transmitting the 9th bit in modes 2 and 3. It is set to transmit a logic 1 in the 9th bit.
- RB8 - Receiver bit 8 or the 9th bit received in modes 2 and 3. Cleared by hardware if 9th bit received is a logic 0. Set by hardware if 9th bit received is a logic 1.
- TI - Transmit Interrupt flag is automatically set at the moment the last bit of one byte is sent. It's a signal to the processor that the line is available for a new byte to transmit. It must be cleared from within the software.
- RI - Receive Interrupt flag is automatically set upon one-byte receive. It signals that byte is received and should be read quickly prior to being replaced by a new data. This bit is also cleared from within the software.
| TMOD | |||||||
| Timer1 | Timer 0 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| Gate | C/T | M1 | M0 | Gate | C/T | M1 | M0 |
- Gate Control
0 = Timer enabled
1 = Timer enabled if INTx\ is high
- C/T:Counter or Timer Selector
0 = Internal count source (clock/12)
1 = External count source (Tx pin)
- M1-M0:Mode Control
00-Mode 0, 13 bit count mode
01-Mode 1, 16 bit count mode
10-Mode 2, Auto reload mode
11-Mode 3, Multiple mode
| TCON | |||||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| TF1 | TR1 | TF0 | TR0 |
- TRx: Timer x run control
0 = Timer not running
1 = Timer running
- TFx: Timer x OverFlow flag
0 = Timer has not overflowed/rolled over
1 = Timer has overflowed/rolled over
Baud Rate Calculation
The main criteria for UART communication is its baud rate. Both the devices Rx/Tx should be set to same baud rate for successful communication.
For the 8051 the Timer 1' is used to generate the baud rate in Auto reload mode.
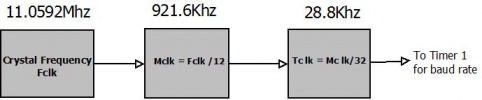
The crystal frequency Fclk is divided by 12 internally which is used to execute instructions also known as Machine Clock. Mclk. The timer again divides the Mclk by 32 and uses it as the timer frequency, say Tclk.
Usually, an 11.0592 Mhz crystal oscillator is used to provide the clock to 8051. The value seems to be odd but we see how it makes sense.
From above discussion
Mclk = Fclk / 12 = 11.0592MHz/12 = 921.6KHz
Tclk = Mclk/32= 921.6KHz/32 = 28.8KHz
If we look at the standard baud rates used for serial communication shown in the table below, we can observe that all the baud rates are factors or multiples of the Tclk (28.8K)! This results in low error rates and hence is a commonly used crystal with 8051.
| Baud Rate | Factor) |
|---|---|
| 2400 | Tclk/12 |
| 4800 | Tclk/6 |
| 9600 | Tclk/3 |
| 14400 | Tclk/2 |
The above factors should be loaded to Timer1(TH1) in Mode2 in order to generate the required baud rate. The final formula for baud rate is as below. Baudrate = Fosc/(32 * 12 * (256-TH1)) $$TH1 = 256 - (Fosc/(32 * 12 * Baudrate))$$ //If( SMOD==0 in PCON register) $$TH1 = 256 - (Fosc/(32 * 6 * Baudrate))$$ //If( SMOD==1 in PCON register)
Now with Fosc = 11.0592Mhz, TH1 value for 9600 baudrate will be: TH1 = 256-(11.0592*10^6)/(32 * 12 * 9600) = 253 = 0xFD = -3
Uart Init Steps
- Select the 8-bit , 1-Start and 1-Stop bit mode in SMOD
- Configure the Timer1 for auto reload mode(Mode-2)
- Load the baud rate generator value to TH1
- Start the Timer for baudrate generation
| void UART_Init(int baudrate) | |
| { | |
| SCON = 0x50; // Asynchronous mode, 8-bit data and 1-stop bit | |
| TMOD = 0x20; //Timer1 in Mode2. | |
| TH1 = 256 - (11059200UL)/(long)(32*12*baudrate); // Load timer value for baudrate generation | |
| TR1 = 1; //Turn ON the timer for Baud rate generation | |
| } |
Steps To Send Char
- Load the new char to be transmitted int SBUF.
- Wait till the char is transmitted. TI will be set when the data in SBUF is transmitted.
- Clear the TI for next cycle.
| void UART_TxChar(char ch) | |
| { | |
| SBUF = ch; // Load the data to be transmitted | |
| while(TI==0); // Wait till the data is trasmitted | |
| TI = 0; //Clear the Tx flag for next cycle. | |
| } |
Steps To Receive Char
- Wait till the Data is received. RI will be set once the data is received in SBUF register.
- Clear the receiver flag(RI) for next cycle.
- Copy/Read the received data from SBUF register.
| char UART_RxChar(void) | |
| { | |
| while(RI==0); // Wait till the data is received | |
| RI=0; // Clear Receive Interrupt Flag for next cycle | |
| return(SBUF); // return the received char | |
| } |
Code
Below is the sample code to Transmit and receive the chars at 9600 baudrate with 11.0592Mhz clock.
| #include<reg51.h> | |
| void UART_Init(int baudrate) | |
| { | |
| SCON = 0x50; // Asynchronous mode, 8-bit data and 1-stop bit | |
| TMOD = 0x20; //Timer1 in Mode2. | |
| TH1 = 256 - (11059200UL)/(long)(32*12*baudrate); // Load timer value for baudrate generation | |
| TR1 = 1; //Turn ON the timer for Baud rate generation | |
| } | |
| void UART_TxChar(char ch) | |
| { | |
| SBUF = ch; // Load the data to be transmitted | |
| while(TI==0); // Wait till the data is trasmitted | |
| TI = 0; //Clear the Tx flag for next cycle. | |
| } | |
| char UART_RxChar(void) | |
| { | |
| while(RI==0); // Wait till the data is received | |
| RI=0; // Clear Receive Interrupt Flag for next cycle | |
| return(SBUF); // return the received char | |
| } | |
| int main() | |
| { | |
| char i,a[]={"Welcome to 8051 Serial Comm, Type the char to be echoed: "}; | |
| char ch; | |
| UART_Init(9600); //Initialize the UART module with 9600 baud rate | |
| for(i=0;a[i]!=0;i++) | |
| { | |
| UART_TxChar(a[i]); // Transmit predefined string | |
| } | |
| while(1) | |
| { | |
| ch = UART_RxChar(); // Receive a char from serial port | |
| UART_TxChar(ch); // Transmit the received char | |
| } | |
| } |
Using ExploreEmbedded Libraries
In the above tutorial we discussed how to configure and use the inbuilt 8051 UART.
Now we will see how to use the ExploreEmbededd UART library.
For this you have to include the uart.c/uart.h files and associated gpio/stdutils files.
- Note:Refer the uart.h file for more info.
| #include "uart.h" | |
| int main() | |
| { | |
| UART_Init(9600); | |
| while(1) | |
| { | |
| UART_Printf("Welcome to 8051 Serial Programming by ExploreEmbedded\n\r"); | |
| } | |
| return (0); | |
| } |
Downloads
Download the sample code and design files from this link.
Have an opinion, suggestion , question or feedback about the article let it out here!