AVR Timer Interrupts
Contents
[hide]Basics
We have covered the basics of AVR timer Programming, during the Timer 1 example we saw that we had to monitor the Flags to check if the Timer has overflown which made the main program dependent on the status of the flags. Timers are independent unit's inside a micro-controller and to make full use of them we will configure and use them with Interrupts. This makes the CPU free from polling the flags and timers can operate on their own. When the timing task is finished, it will interrupt and inform the CPU.
For timer zero, the count goes from 0 to 255 and rolls over. With that the timer over flow flag is set and it can be used to trigger an interrupt.
Let us repeat the same example of blinking a LED connected to PD4 at 100ms delay with Timer 1 but this time using Interrupts. We have covered the Basics of AVR Interrupts, you may wish to go through it first.
All the calculations from the previous tutorial hold good. Except, since we are using the Timer OverFlow flag, the value 65536 - 1562 = 63974 is loaded in TCNT1.
Steps to configure the Timer Interrupt:
- Load the TCNT1 register with the value calculated above.
- Set CS10 and CS12 bits to configure pre-scalar of 1024
- Enable timer1 overflow interrupt(TOIE1), the register is shown below
- Enable global interrupts by setting global interrupt enable bit in SREG
- Toggle the LED in the ISR and reload the TCNT value.
| TIMSK | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| - | - | TICIE1 | OCIE1A | OCIE1B | TOIE1 | - | - |
Code
| #include<avr/io.h> | |
| #include<avr/interrupt.h> | |
| #define LED PD4 | |
| ISR (TIMER1_OVF_vect) // Timer1 ISR | |
| { | |
| PORTD ^= (1 << LED); | |
| TCNT1 = 63974; // for 1 sec at 16 MHz | |
| } | |
| int main() | |
| { | |
| DDRD = (0x01 << LED); //Configure the PORTD4 as output | |
| TCNT1 = 63974; // for 1 sec at 16 MHz | |
| TCCR1A = 0x00; | |
| TCCR1B = (1<<CS10) | (1<<CS12);; // Timer mode with 1024 prescler | |
| TIMSK = (1 << TOIE1) ; // Enable timer1 overflow interrupt(TOIE1) | |
| sei(); // Enable global interrupts by setting global interrupt enable bit in SREG | |
| while(1) | |
| { | |
| } | |
| } | |
Look at the while(1) loop, it is happy that there is no code to execute in there ;)
Video Tutorial
For those of you, who would like to watch instead of read we have made a video with all the gyan.
Downloads
Download the complete project folder from the below link:
https://github.com/ExploreEmbedded/ATmega32_ExploreUltraAvrDevKit/archive/master.zip
Have a opinion, suggestion , question or feedback about the article let it out here!
AVR I/O Register Configuration
In this tutorial we are going to discuss the port configuration of AVR/Atmel controllers or in general Atmega family. In this tutorial we will be using Atmega32 as reference, same will be applicable...

Basics of AVR 'C'
Let us look at the basics of 'C' for programming AVR Micrcontrollers in this tutorial. Simple stuff like setting and clearing bits is important to any project you do. It is often required to set...
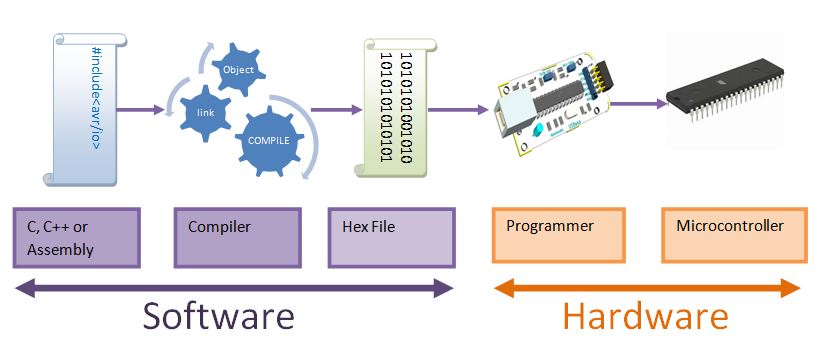
AVR Hardware and Software Setup
In this tutorial we will look at the basic setup required to get started with AVR series of microcontrollers. There are two aspects to it, the software and the hardware. Fortunately, we for AVR...

AVR Timer programming
Basics Timers come in handy when you want to set some time interval like your alarm. This can be very precise to a few microseconds. Timers/Counters are essential part of any modern...

